208. Implement Trie
문제
A trie (pronounced as "try") or prefix tree is a tree data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete and spellchecker.
Implement the Trie class:
Trie()Initializes the trie object.void insert(String word)Inserts the string word into the trie.boolean search(String word)Returns true if the string word is in the trie (i.e., was inserted before), and false otherwise.boolean startsWith(String prefix)Returns true if there is a previously inserted string word that has the prefix prefix, and false otherwise.
예제 입출력
Input
["Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"]
[[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]]
Output
[null, null, true, false, true, null, true]
Explanation
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // return True
trie.search("app"); // return False
trie.startsWith("app"); // return True
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // return True
참고
You can read the full description here.
풀이 1
접근법
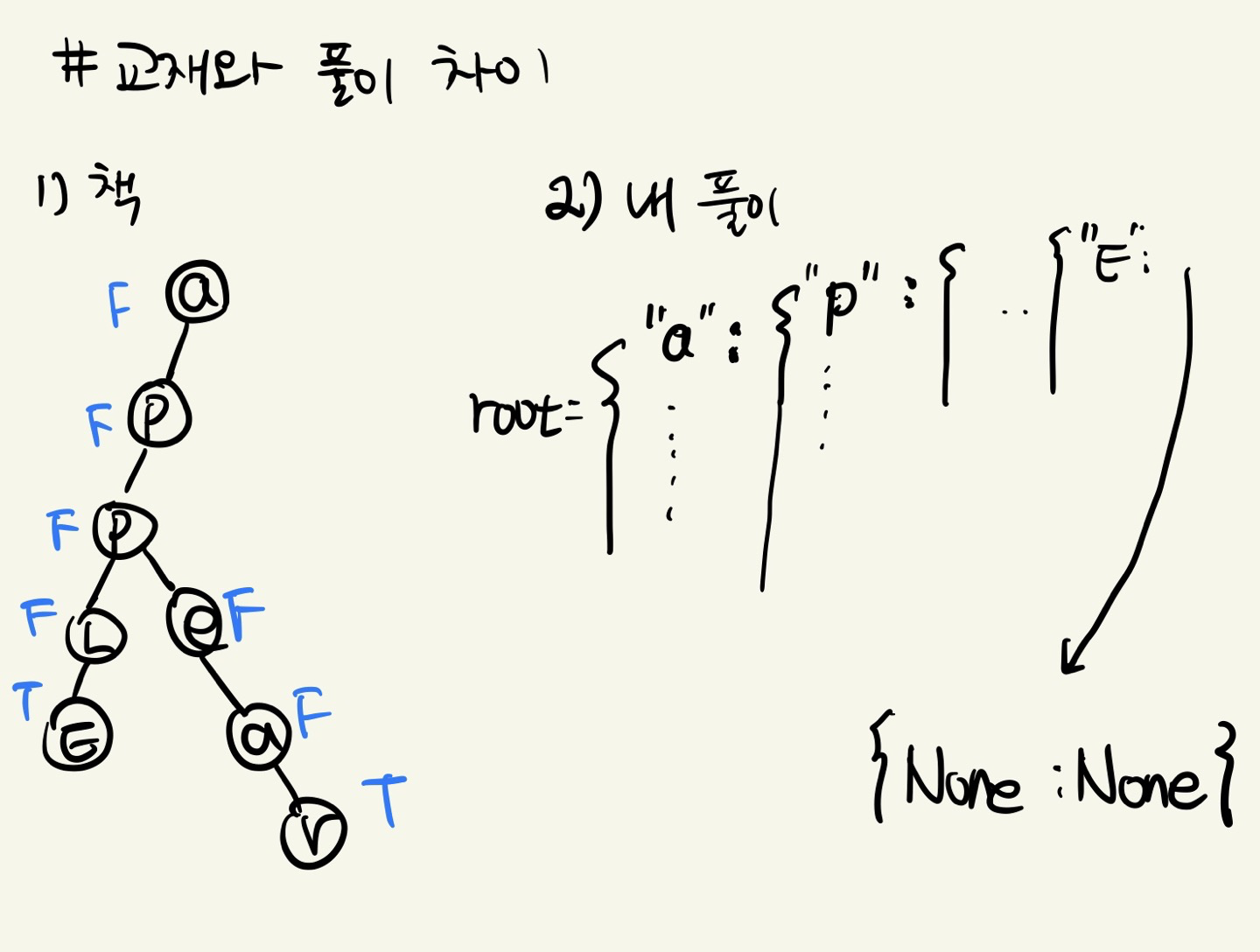
defaultdict를 이용해 구현합니다.init: root를 초기화합니다.insert: 현재 노드에 현재 단어의 key가 있으면 노드를 갱신해줍니다. 없으면 새로운 키 - 값 쌍을 만듭니다.- insert 과정 중 삽입이 완료 되었으면 해당 위치에 None - None 으로 키 - 값 쌍을 추가합니다.
startsWith,search: 트라이를 순회하면서 성공 실패 여부를 체크합니다. search의 경우 None 값이 있는지 체크합니다.
구현 코드
from collections import defaultdict
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = defaultdict(dict)
def insert(self, word: str) -> None:
word = list(word)[::-1]
cur_node = self.root
while(word):
cur_word = word.pop()
if cur_word not in set(cur_node.keys()):
cur_node[cur_word] = defaultdict(dict)
cur_node = cur_node[cur_word]
cur_node[None] = None
def search(self, word: str) -> bool:
word = list(word)[::-1]
cur_node = self.root
while(word):
cur_word = word.pop()
if cur_word not in set(cur_node.keys()):
return False
cur_node = cur_node[cur_word]
if None in cur_node:
return True
else:
return False
def startsWith(self, prefix: str) -> bool:
word = list(prefix)[::-1]
cur_node = self.root
while(word):
cur_word = word.pop()
if cur_word not in set(cur_node.keys()):
return False
cur_node = cur_node[cur_word]
return True
복잡도 분석
- : 단어 길이
- 시간복잡도:
책에 있는 풀이
참고
원본 코드는 여기에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
풀이 2
접근법
TrieNode클래스를 별도로 선언합니다.- 단어가 끝나는 부분에
True로 체크를 해줍니다.
구현 코드
import collections
# 트라이의 노드
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.word = False
self.children = collections.defaultdict(TrieNode)
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
# 단어 삽입
def insert(self, word: str) -> None:
node = self.root
for char in word:
node = node.children[char]
node.word = True
# 단어 존재 여부 판별
def search(self, word: str) -> bool:
node = self.root
for char in word:
if char not in node.children:
return False
node = node.children[char]
return node.word
# 문자열로 시작 단어 존재 여부 판별
def startsWith(self, prefix: str) -> bool:
node = self.root
for char in prefix:
if char not in node.children:
return False
node = node.children[char]
return True
참고용 그림